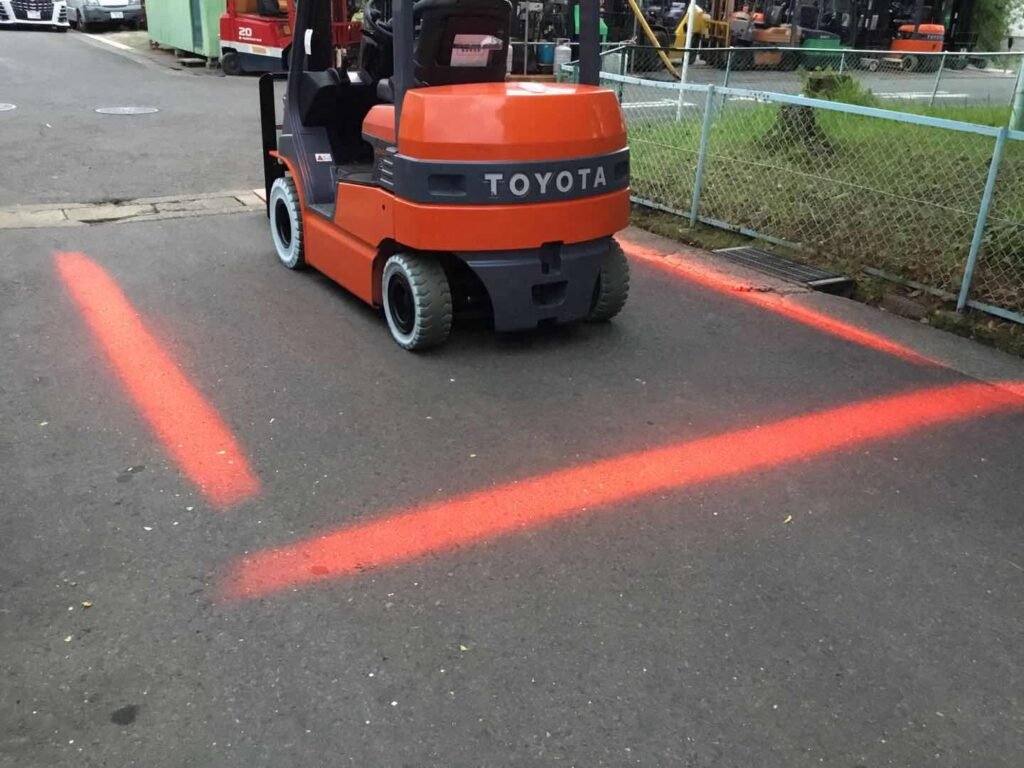
Forklifts are indispensable tools in warehouses, factories, and construction sites, making heavy lifting and transportation easier and more efficient. However, when improperly operated or maintained, forklifts pose significant safety risks. Ensuring safe forklift operation is critical for preventing accidents and maintaining a productive work environment. This comprehensive Forklift Operation Safety Guide will cover everything you need to know about operating a forklift safely, offering forklift safety tips, best practices, and essential knowledge on forklift basics.
Table of Contents
1. Why Are Forklift Accidents So Frequent?
Despite the advantages forklifts provide, accidents involving these machines are unfortunately common. Understanding the root causes of forklift accidents is essential to mitigate risk and create a safer workplace. Some of the primary reasons for forklift accidents include improper operation, overloading, and visibility issues.

1.1 Improper Forklift Operation and Maintenance
Improper operation and poor maintenance are among the leading causes of forklift accidents. When operators are not well-trained or fail to follow forklift safety tips, the risk of accidents increases. Operating a forklift requires attention to detail, proper knowledge of controls, and an understanding of safe maneuvering techniques. Forklifts that are not maintained correctly may also malfunction, leading to unsafe working conditions.
Regular inspections and adherence to safety standards can prevent accidents that stem from poor maintenance. Every operator must be trained in forklift safe operation practices and know how to check the forklift for issues before starting their shift.
1.2 Overloading
Overloading the forklift is another common cause of accidents. Every forklift has a specific weight capacity, and exceeding that limit can cause the forklift to tip over. Additionally, an overloaded forklift is harder to control, which can increase the risk of accidents. How to operate a forklift safely requires understanding the load limit and adhering to it at all times.
1.3 Obstacles Restricting Vision
Many forklift accidents occur because of obstacles obstructing the operator’s view. Forklifts often have large loads in front of them, making it difficult for the operator to see pedestrians or obstacles in the path. This is why it’s critical to ensure that your forklift is equipped with safety lights and that operators use their mirrors and take extra care when driving in narrow aisles or around blind corners.
1.4 Strictly Comply with Safety Regulations
Forklifts are regulated by safety standards to ensure that they are used safely. These regulations are designed to protect both operators and workers nearby. Strict adherence to these safety guidelines is crucial for preventing accidents. Operators must be familiar with the forklift operation regulations and always follow them.
2. Forklift Safe Operation Steps
There are four key aspects to improving forklift operation safety. By focusing on each of these, you can significantly reduce the risk of accidents in the workplace.
2.1 Ensure the Forklift is in a Safe Driving State
Before operating a forklift, it is essential to check that the forklift is in good working condition. This includes ensuring that the tires are properly inflated, the brakes are functioning, and there are no leaks in the hydraulic system. A forklift in disrepair is a safety hazard, so forklift maintenance is vital.
2.2 Master the Essentials of Safe Forklift Driving
Operating a forklift requires skill and precision. Key components of safe forklift operation include:
- Maintaining a stable speed and stopping distance.
- Keeping the load at a safe height and properly balanced.
- Using both hands on the steering wheel for maximum control.
- Never allowing the forklift to travel with an elevated load unless absolutely necessary.
2.3 Know How to Load and Unload Goods Correctly
Loading and unloading are the most common activities for forklifts, but they come with their own set of risks. Always ensure that the load is evenly distributed on the forklift’s forks, and never exceed the forklift’s maximum load capacity. The forklift must be stable when lifting heavy loads, and operators should never rush these tasks.
2.4 Pay Attention to Daily Maintenance and Reasonable Forklift Scrapping
Routine maintenance and regular inspections are critical to forklift safe operation. Operators should check the forklift’s tires, hydraulic system, and other components before each shift. A well-maintained forklift is far less likely to experience mechanical failure or accidents.
3. Pre-Operation Inspection of Forklift
The pre-operation inspection is a fundamental step in ensuring that the forklift is safe to use. Regularly checking all aspects of the forklift can help detect problems before they cause accidents.

3.1 Visual Inspection of Forklift Components
Start by visually inspecting key components of the forklift, including the forks, mast, and tires. Look for any signs of damage or wear. A cracked fork or worn tire can significantly affect the forklift’s performance and safety.
3.2 Checking Oil Level and Gauges
Check the hydraulic oil level and ensure all gauges are functioning correctly. The oil level should be adequate to maintain the lifting power of the forklift. Additionally, check the fuel level, lights, and any other indicators on the dashboard.
3.3 Operational Inspection with Engine Running
With the engine running, test all the forklift’s controls, including the steering, lift, and tilt functions. Ensure that the forklift operates smoothly without any unusual sounds or jerks. This will help identify potential issues before operation begins.
4. Understanding Basic Forklift Controls and Gauges
Before operating a forklift, it’s crucial to understand the basic controls and gauges. Each forklift may have a slightly different configuration, but generally, these are the essential components to know.
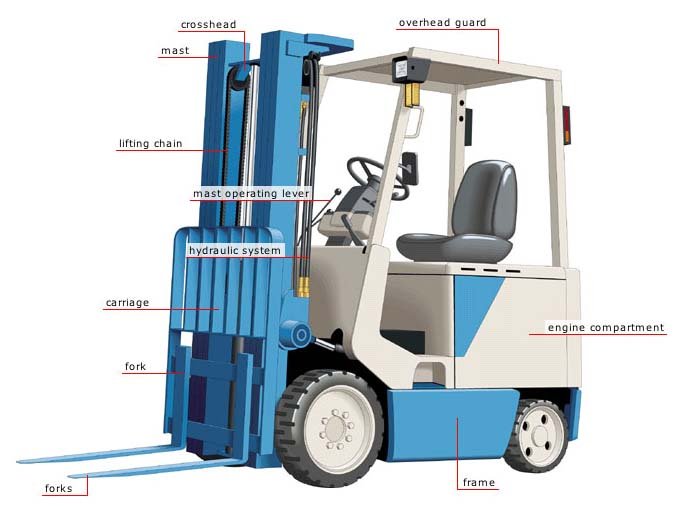

4.1 Steering and Maneuvering Controls
The steering wheel controls the direction of the forklift, while the pedals manage speed and braking. Familiarize yourself with the responsiveness of these controls and ensure that they work smoothly.
4.2 Lift and Tilt Controls
The lift and tilt controls are used to raise, lower, and tilt the mast of the forklift. How to use a forklift efficiently involves operating these controls to load, unload, and transport materials safely.
4.3 Forklift Dashboard Gauges and Indicators
Forklifts have a range of gauges and warning lights on the dashboard to monitor the vehicle’s performance. These may include temperature, fuel, and battery gauges. Pay attention to these indicators and take immediate action if any warning lights appear.
5. Learn Safe Forklift Operating Techniques
Knowing the best forklift tips for safe operation can help prevent accidents. Here are some critical safe operating techniques:
5.1 Maintain Proper Load Balance
Properly balancing the load on the forklift is essential to avoid tipping. Always ensure that the load is centered on the forks and is stable before moving it. Forklift safe operation requires that the load is always secured and never overhanging from the forklift.
5.2 Navigating Tight Spaces and Turns
When navigating tight spaces, always slow down and make wide, careful turns. Keep the load low and in sight to avoid hitting obstacles or pedestrians.
5.3 Driving at a Safe Speed
Driving at a safe speed is crucial for preventing accidents. Always adjust your speed based on the load you are carrying, the environment, and the traffic around you. Never exceed the maximum speed limit posted in the work area.
6. How to Operate a Forklift: Lifting a Load
Lifting a load requires careful planning and attention to safety. Here are the essential steps:

6.1 Preparing to Lift a Load Safely
Before lifting any load, ensure that the area is clear of pedestrians, obstacles, and other vehicles. Use your horn to alert others if necessary. Ensure the load is stable and well-balanced on the forks.
6.2 Approaching a Load with a Forklift
When approaching a load, drive the forklift straight into the pallet or material, ensuring the forks are properly aligned.
6.3 Mast Position on a Forklift
Keep the mast tilted back when transporting a load. This helps prevent the load from shifting and falling.
6.4 Positioning the Forks to Prepare for Lifting a Load
Position the forks beneath the load, ensuring they are evenly spaced and fully engaged with the pallet. Slowly lift the load, ensuring it remains stable and balanced.
6.5 High Stacking
When stacking loads, ensure the forklift is on level ground and that the load is balanced. Never stack loads higher than the forklift’s maximum stacking height.
6.6 Tip-over Safety and Response
If the forklift begins to tip, stay inside the cab and hold on tightly. Do not jump out of the forklift, as this can result in serious injury.
7. How to Operate a Forklift: Maintenance and Decommissioning
Regular maintenance is essential for safe forklift operation. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for routine servicing and repairs. When a forklift reaches the end of its useful life, decommission it and replace it with a newer, safer model.
8.Forklift lighting – one of the key elements of forklift operating safety
One effective way to increase forklift operating safety is to use safety lighting. Forklift safety lighting is essential to improve visibility and ensure operators are aware of their surroundings, especially in low light or heavy traffic environments.
8.1Benefits of Improving Forklift Operation Safety with Lighting
a. Improved Worker Safety
The most significant benefit of forklift safety lighting is the enhancement of worker safety. By ensuring that forklifts are easily visible, safety lighting reduces the likelihood of accidents involving pedestrians, other vehicles, or equipment. This is particularly important in areas where employees work in close proximity to forklifts, such as warehouse aisles, construction zones, or factory floors.
b. Increased Awareness of Forklift Movements
Proper safety lighting provides a clear indication of when a forklift is moving, where it is going, and what direction it’s facing. This awareness helps to prevent unexpected collisions and ensures that workers can take appropriate precautions when interacting with forklifts. For example, pedestrian safety lights project a beam of light on the ground to warn pedestrians of an approaching forklift, encouraging them to keep their distance.
c. Reduced Risk of Accidents and Injuries
By improving the visibility of both the forklift and its operator, the use of safety lights significantly reduces the risk of accidents and injuries. Forklift accidents are among the most common workplace incidents, and the proper use of lighting systems can minimize these risks. This leads to fewer accidents, reduced medical costs, and fewer days lost due to injury.
d. Enhanced Operational Efficiency
When forklifts are equipped with the right lighting systems, operators are able to navigate more efficiently and safely, particularly in low-light conditions or areas with limited visibility. This improved visibility leads to smoother operations, faster task completion, and a more organized work environment.
e. Compliance with Safety Standards
Many regulatory bodies, such as OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) in the United States, have specific guidelines for forklift operation, including the use of safety lighting. By installing the correct lighting systems, businesses can ensure they meet legal requirements and avoid penalties for non-compliance.
8.2 Types of Forklift Safety Lighting
1. Forklift Warning Lights
Warning lights are one of the most common types of forklift safety lighting. These lights are designed to alert pedestrians and other workers in the area of the forklift’s presence. Warning lights are typically mounted at the front, rear, or sides of the forklift.
- Beacon Lights: These are rotating or flashing lights that provide a highly visible warning to others. They are particularly useful in environments with high traffic, such as warehouses or construction sites, where the forklift may be moving quickly.
- Flashing Warning Lights: These lights flash in a bright, eye-catching pattern, warning others of the forklift’s movement. They are typically mounted at the top of the forklift and can be visible from a distance.
- LED Safety Lights: Modern LED warning lights are energy-efficient, long-lasting, and provide bright illumination. They are often preferred due to their low energy consumption and durability.
2. Forklift Strobe Lights
Strobe lights are intense, high-frequency flashing lights that are extremely effective in alerting people of the forklift’s presence. Strobe lights are often used in environments where visibility is poor, such as dark or foggy conditions. Their bright, flashing nature ensures that the operator and pedestrians can see the forklift from a significant distance, especially in busy or crowded areas.
3. Forklift Spotlight/Work Lights
Spotlights or work lights are mounted on forklifts to illuminate the operator’s surroundings. These lights help to improve visibility when operating the forklift in low-light conditions. Spotlights can be positioned at various angles and may have adjustable settings, allowing the operator to focus light where it’s most needed, such as when maneuvering in tight spaces.
- Floodlights: These lights provide broad, even illumination over a larger area, helping operators see obstacles and avoid accidents while navigating.
- Spotlights: These lights focus on a narrow area, offering concentrated lighting for precision tasks.
4. Forklift Pedestrian Warning Lights
Pedestrian warning lights are mounted on forklifts to alert people walking or working near the forklift. These lights are often projected onto the floor or ground, creating a visible light zone that warns pedestrians to stay clear of the forklift’s path.
- Blue Spotlights: These are often projected in a circle or line on the floor in front or behind the forklift, signaling the operator’s movement and warning pedestrians to stay out of the area.
- Red Safety Lights: These lights project red beams on the ground, similar to blue spotlights, to provide clear warning signs to nearby workers.
5. Forklift Back-up Lights
Back-up lights are essential for safe forklift operation in areas where forklifts frequently reverse or operate in confined spaces. These lights illuminate the area behind the forklift and provide additional visibility for the operator when moving in reverse. They can also alert pedestrians and other operators to the forklift’s movement.
6. Forklift Floor Lights
Floor lights are designed to project a light pattern onto the ground near the forklift’s wheels. These lights help operators see the area directly in front or behind the forklift, improving safety when driving in tight spaces or while maneuvering through racks and aisles. They also enhance visibility for pedestrians, helping them avoid walking into the path of the forklift.
9. Things to Note When Operating a Forklift
.jpg)
9.1 Properly Securing Loads
Ensure that loads are properly secured before moving. Unstable loads can shift during transport and cause accidents.
9.2 Maintaining Proper Loading Height
Always maintain the load at a safe height, usually a few inches above the ground. This ensures that the forklift remains stable and the load doesn’t interfere with visibility.
9.3 Tilt the Forks Back When Loading
Tilting the forks back helps secure the load and prevents it from slipping.
9.4 Use Proper Climbing Techniques
When navigating ramps or uneven surfaces, use the correct technique. Always drive the forklift forward when going up a ramp and backward when going down.
10. Things to Avoid When Operating a Forklift
10.1 Lifting Heavy Objects While Moving
Never lift heavy objects while the forklift is moving. This can make the forklift unstable and lead to accidents.
10.2 Driving with an Elevated Load
Driving with an elevated load is dangerous, as it can affect the stability of the forklift.
10.3 Failing to Use the Forklift’s Safety Features
Always use the forklift’s safety features, such as lights, mirrors, and seat belts, to ensure the safety of the operator and others.
11. FAQ
11.1 What is a forklift safety checklist?
The forklift safety checklist includes checking brakes, tires and fluid levels, checking lights and horn, and ensuring load stability. Completing a pre-operation inspection is essential to identifying and addressing potential hazards before use. Make a habit of following this safety checklist to reduce the risk of accidents.
11.2 What are the important rules to remember when operating a forklift?
You must wear appropriate personal protective equipment, maintain a safe distance from pedestrians, and avoid sudden stops or starts. You should always obey speed limits, maintain a clear field of vision, and drive in designated areas. If you follow these safety practices, you can avoid the risk of injury to others and yourself. So, follow all safety procedures and ensure a safer working environment.
11.3 What are the three pedals on a forklift for?
The accelerator pedal moves forward or backward; the brake pedal stops movement; and the inching pedal provides precise control during loading/unloading tasks.
11.4 Can a forklift be considered unattended even if it is within the operator's field of vision?
Yes, a forklift is considered unattended if the operator is 25 feet away from the forklift, even if the forklift is within the operator’s field of vision.
12.Conclusion: Forklift Operation Safety
To summarize, forklift operation safety is paramount for both the operators and those working in the surrounding environment. By ensuring that the forklift is in proper working condition, maintaining a clear and organized workplace, and adhering to safe forklift operation practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of accidents. Always prioritize forklift safety tips, undergo proper training, and follow safety regulations to ensure a safe working environment.

-1024x683.jpg)